OpenCV + NPU 源码解析
完整的代码已经上传Github开源,前往以下地址:https://github.com/YuzukiHD/TinyVision/tree/main/tina/openwrt/package/thirdparty/vision/opencv_camera_mobilenet_v2_ssd/src
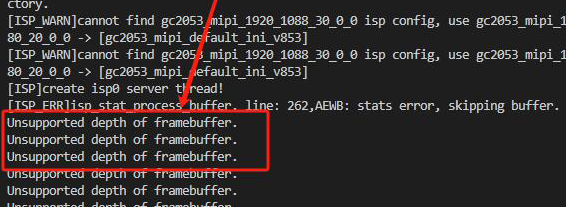
否则报错 Unsupported depth of framebuffer
Mobilenet v2 前处理
void get_input_data(const cv::Mat& sample, uint8_t* input_data, int input_h, int input_w, const float* mean, const float* scale){
cv::Mat img;
if (sample.channels() == 1)
cv::cvtColor(sample, img, cv::COLOR_GRAY2RGB);
else
cv::cvtColor(sample, img, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB);
cv::resize(img, img, cv::Size(input_h, input_w));
uint8_t* img_data = img.data;
/* nhwc to nchw */
for (int h = 0; h < input_h; h++) {
for (int w = 0; w < input_w; w++) {
for (int c = 0; c < 3; c++) {
int in_index = h * input_w * 3 + w * 3 + c;
int out_index = c * input_h * input_w + h * input_w + w;
input_data[out_index] = (uint8_t)(img_data[in_index]); //uint8
}
}
}
}
uint8_t *mbv2_ssd_preprocess(const cv::Mat& sample, int input_size, int img_channel) {
const float mean[3] = {127, 127, 127};
const float scale[3] = {0.0078125, 0.0078125, 0.0078125};
int img_size = input_size * input_size * img_channel;
uint8_t *tensor_data = NULL;
tensor_data = (uint8_t *)malloc(1 * img_size * sizeof(uint8_t));
get_input_data(sample, tensor_data, input_size, input_size, mean, scale);
return tensor_data;
}
这段C++代码是用于对输入图像进行预处理,以便输入到MobileNet V2 SSD模型中进行目标检测。
-
get_input_data函数:- 该函数对输入的图像进行预处理,将其转换为适合MobileNet V2 SSD模型输入的格式。
- 首先,对输入图像进行通道格式的转换,确保图像通道顺序符合模型要求(RGB格式)。
- 然后,将图像大小调整为指定的输入尺寸(
input_h * input_w)。 - 最后,将处理后的图像数据按照特定顺序(NCHW格式)填充到
input_data数组中,以便作为模型的输入数据使用。
-
mbv2_ssd_preprocess函数:- 该函数是对输入图像进行 MobileNet V2 SSD 模型的预处理,并返回处理后的数据。
- 在函数内部,首先定义了图像各通道的均值(mean)和缩放比例(scale)。
- 然后计算了输入图像的总大小,并分配了相应大小的内存空间用于存储预处理后的��数据。
- 调用了
get_input_data函数对输入图像进行预处理,将处理后的数据存储在tensor_data中,并最终返回该数据指针。
总的来说,这段代码的功能是将输入图像进行预处理,以适应MobileNet V2 SSD模型的输入要求,并返回预处理后的数据供模型使用。同时需要注意,在使用完tensor_data后,需要在适当的时候释放相应的内存空间,以避免内存泄漏问题。
Mobilenet v2 后处理
这部分分为来讲:
// 比较函数,用于按照分数对Bbox_t对象进行排序
bool comp(const Bbox_t &a, const Bbox_t &b) {
return a.score > b.score;
}
// 计算两个框之间的交集面积
static inline float intersection_area(const Bbox_t& a, const Bbox_t& b) {
// 将框表示为cv::Rect_<float>对象
cv::Rect_<float> rect_a(a.xmin, a.ymin, a.xmax-a.xmin, a.ymax-a.ymin);
cv::Rect_<float> rect_b(b.xmin, b.ymin, b.xmax-b.xmin, b.ymax-b.ymin);
// 计算两个矩形的交集
cv::Rect_<float> inter = rect_a & rect_b;
// 返回交集的面积
return inter.area();
}
// 非极大值抑制算法(NMS)
static void nms_sorted_bboxes(const std::vector<Bbox_t>& bboxs, std::vector<int>& picked, float nms_threshold) {
picked.clear();
const int n = bboxs.size();
// 创建存储每个框面积的向量
std::vector<float> areas(n);
// 计算每个框的面积并存储
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
areas[i] = (bboxs[i].xmax - bboxs[i].xmin) * (bboxs[i].ymax - bboxs[i].ymin);
}
// 对每个框进行遍历
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
const Bbox_t& a = bboxs[i];
int keep = 1;
// 对已经选择的框进行遍历
for (int j = 0; j < (int)picked.size(); j++) {
const Bbox_t& b = bboxs[picked[j]];
// 计算交集和并集面积
float inter_area = intersection_area(a, b);
float union_area = areas[i] + areas[picked[j]] - inter_area;
// 计算交并比
if (inter_area / union_area > nms_threshold)
keep = 0; // 如果交并比大于阈值,则不选择该框
}
// 如果符合条件则选择该框,加入到结果向量中
if (keep)
picked.push_back(i);
}
}
这段代码实现了目标检测中常用的非极大值抑制算法(NMS)。comp函数用于对Bbox_t对象按照分数进行降序排序。intersection_area函数用于计算两个框之间的交集面积。nms_sorted_bboxes函数是NMS算法的具体实现,它接受一个已经按照分数排序的框的向量bboxs,以及一个空的整数向量picked,用于存储保留下来的框的索引。nms_threshold是一个阈值,用于控制重叠度。
算法的步骤如下:
- 清空存储结果的
picked向量。 - 获取框的个数
n,创建一个用于存储每个框面积的向量areas。 - 遍历每个框,计算其面积并存储到
areas向量中。 - 对每个框进行遍历,通过计算交并比来判断是否选择该框。如果交并比大于阈值,则不选择该框。
- 如果符合条件,则选择该框,将其索引加入到
picked向量中。 - 完成非极大值抑制算法,
picked向量中存储了保留下来的框的索引。
这个算法的作用是去除高度重叠的框,只保留得分最高的那个框,以减少冗余检测结果。
cv::Mat detect_ssd(const cv::Mat& bgr, float **output) {
// 定义阈值和常数
float iou_threshold = 0.45;
float conf_threshold = 0.5;
const int inputH = 300;
const int inputW = 300;
const int outputClsSize = 21;
#if MBV2_SSD
int output_dim_1 = 3000;
#else
int output_dim_1 = 8732;
#endif
// 计算输出数据的大小
int size0 = 1 * output_dim_1 * outputClsSize;
int size1 = 1 * output_dim_1 * 4;
// 将输出数据转换为向量
std::vector<float> scores_data(output[0], &output[0][size0-1]);
std::vector<float> boxes_data(output[1], &output[1][size1-1]);
// 获取分数和边界框的指针
const float* scores = scores_data.data();
const float* bboxes = boxes_data.data();
// 计算缩放比例
float scale_w = bgr.cols / (float)inputW;
float scale_h = bgr.rows / (float)inputH;
bool pass = true;
// 创建存储检测结果的向量
std::vector<Bbox_t> BBox;
// 遍历每个框
for(int i = 0; i < output_dim_1; i++) {
std::vector<float> conf;
// 获取每个框的置信度
for(int j = 0; j < outputClsSize; j++) {
conf.emplace_back(scores[i * outputClsSize + j]);
}
// 找到置信度最大的类别
int max_index = std::max_element(conf.begin(), conf.end()) - conf.begin();
// 如果类别不是背景类,并且置信度大于阈值,则选中该框
if (max_index != 0) {
if(conf[max_index] < conf_threshold)
continue;
Bbox_t b;
// 根据缩放比例计算框的坐标和尺寸
int left = bboxes[i * 4] * scale_w * 300;
int top = bboxes[i * 4 + 1] * scale_h * 300;
int right = bboxes[ i * 4 + 2] * scale_w * 300;
int bottom = bboxes[i * 4 + 3] * scale_h * 300;
// 确保坐标不超出图像范围
b.xmin = std::max(0, left);
b.ymin = std::max(0, top);
b.xmax = right;
b.ymax = bottom;
b.score = conf[max_index];
b.cls_idx = max_index;
BBox.emplace_back(b);
}
conf.clear();
}
// 按照分数对框进行排序
std::sort(BBox.begin(), BBox.end(), comp);
// 应用非极大值抑制算法,获取保留的框的索引
std::vector<int> keep_index;
nms_sorted_bboxes(BBox, keep_index, iou_threshold);
// 创建存储框位置的向量
std::vector<cv::Rect> bbox_per_frame;
// 遍历保留的框,绘制框和标签
for(int i = 0; i < keep_index.size(); i++) {
int left = BBox[keep_index[i]].xmin;
int top = BBox[keep_index[i]].ymin;
int right = BBox[keep_index[i]].xmax;
int bottom = BBox[keep_index[i]].ymax;
int width = right - left;
int height = bottom - top;
int center_x = left + width / 2;
cv::rectangle(bgr, cv::Point(left, top), cv::Point(right, bottom), cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1);
char text[256];
sprintf(text, "%s %.1f%%", class_names[BBox[keep_index[i]].cls_idx], BBox[keep_index[i]].score * 100);
cv::putText(bgr, text, cv::Point(left, top), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 1, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 255), 1, 8, 0);
bbox_per_frame.emplace_back(left, top, width, height);
}
// 返回绘制了框和标签的图像
return bgr;
}
这段代码主要用于处理模型的输出结果,将输出数据转换为向量,并计算缩放比例,然后创建一个向量来存储检测结果。
具体步骤如下:
- 定义了一些阈值和常数,包括IOU阈值(
iou_threshold)、置信度阈值(conf_threshold)、输入图像的高度和宽度(inputH和inputW)、输出类别数量(outputClsSize)、输出维度(output_dim_1)。 - 计算输出数据的大小,分别为类别得分数据的大小(
size0)和边界框数据的大小(size1)。 - 将输出数据转换为向量,分别为类别得分数据向量(
scores_data)和边界框数据向量(boxes_data)。 - 获取类别得分和边界框的指针,分别为
scores和bboxes。 - 计算图像的缩放比例,根据输入图像的尺寸和模型输入尺寸之间的比例计算得到。
- 创建一个向量
BBox,用于存储检测结果。该向量的类型为Bbox_t - 遍历每一个框(共有
output_dim_1个框)。 - 获取每一个框的各个类别的置信度,并将其存储在
conf向量中。 - 找到置信度最大的类别,并记录其下标
max_index。 - 如果最大置信度的类别不是背景类,并且置信度大于设定的阈值,则选中该框。
- 根据缩放比例计算框的坐标和尺寸,其中
left、top、right和bottom分别表示框的左上角和右下角的坐标。 - 确保框的坐标不超出图像范围,并将目标框的信息(包括位置、置信度、类别等)存储在
Bbox_t类型的变量b中。 - 将
b加入到BBox向量中。 - 清空
conf向量,为下一个框的检测做准备。 - 对所有检测到的目标框按照置信度从高到低排序;
- 应用非极大值抑制算法,筛选出重叠度较小的目标框,并将保留的目标框的索引存储在
keep_index向量中; - 遍历保留的目标框,对每个目标框进行绘制和标注;
- 在图像上用矩形框标出目标框的位置和大小,并在矩形框内添加目标类别和置信度;
- 将绘制好的目标框信息(包括左上角坐标、宽度和高度)存储在
bbox_per_frame向量中; - 返回绘制好的图像。
需要注意的是,该代码使用了OpenCV库中提供的绘制矩形框和添加文字的相关函数。其中cv::rectangle()函数用于绘制矩形框,cv::putText()函数用于在矩形框内添加目标类别和置信度。
获取显示屏的参数信息
// 帧缓冲器信息结构体,包括每个像素的位数和虚拟分辨率
struct framebuffer_info {
uint32_t bits_per_pixel;
uint32_t xres_virtual;
};
// 获取帧缓冲器的信息函数,接受设备路径作为参数
struct framebuffer_info get_framebuffer_info(const char* framebuffer_device_path)
{
struct framebuffer_info info;
struct fb_var_screeninfo screen_info;
int fd = -1;
// 打开设备文件
fd = open(framebuffer_device_path, O_RDWR);
// 如果成功打开设备文件,则使用 ioctl 函数获取屏幕信息
if (fd >= 0) {
if (!ioctl(fd, FBIOGET_VSCREENINFO, &screen_info)) {
info.xres_virtual = screen_info.xres_virtual; // 虚拟分辨率
info.bits_per_pixel = screen_info.bits_per_pixel; // 像素位数
}
}
return info;
};
这段代码的用途是获取帧缓冲器的信息。
具体来说:
-
framebuffer_info是一个结构体,用于存储帧缓冲器的信息,包括每个像素的位数和虚拟分辨率。 -
get_framebuffer_info是一个函数,用于获取帧缓冲器的信息。它接受帧缓冲器设备路径作为参数,打开设备文件并使用 ioctl 函数获取屏幕信息,然后将信息存储在framebuffer_info结构体中并返回。
信号处理函数
注册信号处理函数,用于 ctrl-c 之后关闭摄像头,防止下一次使用摄像头出现摄像头仍被占用的情况。
/* Signal handler */
static void terminate(int sig_no)
{
printf("Got signal %d, exiting ...\n", sig_no);
cap.release();
exit(1);
}
static void install_sig_handler(void)
{
signal(SIGBUS, terminate); // 当程序访问一个不合法的内存地址时发送的信号
signal(SIGFPE, terminate); // 浮点异常信号
signal(SIGHUP, terminate); // 终端断开连接信号
signal(SIGILL, terminate); // 非法指令信号
signal(SIGINT, terminate); // 中断进程信号
signal(SIGIOT, terminate); // IOT 陷阱信号
signal(SIGPIPE, terminate); // 管道破裂信号
signal(SIGQUIT, terminate); // 停止进程信号
signal(SIGSEGV, terminate); // 无效的内存引用信号
signal(SIGSYS, terminate); // 非法系统调用信号
signal(SIGTERM, terminate); // 终止进程信号
signal(SIGTRAP, terminate); // 跟踪/断点陷阱信号
signal(SIGUSR1, terminate); // 用户定义信号1
signal(SIGUSR2, terminate); // 用户定义信号2
}
这段代码定义了两个函数,并给出了相应的注释说明。具体注释如下:
static void terminate(int sig_no):信号处理函数。int sig_no:接收到的信号编号。printf("Got signal %d, exiting ...\n", sig_no);:打印接收到的信号编号。cap.release();:释放视频流捕获对象。exit(1);:退出程序。
static void install_sig_handler(void):安装信号处理函数。signal(SIGBUS, terminate);:为SIGBUS信号安装信号处理函数。signal(SIGFPE, terminate);:为SIGFPE信号安装信号处理函数。signal(SIGHUP, terminate);:为SIGHUP信号安装信号处理函数。signal(SIGILL, terminate);:为SIGILL信号安装信号处理函数。signal(SIGINT, terminate);:为SIGINT信号安装信号处理函数。signal(SIGIOT, terminate);:为SIGIOT信号安装信号处理函数。signal(SIGPIPE, terminate);:为SIGPIPE信号安装信号处理函数。signal(SIGQUIT, terminate);:为SIGQUIT信号安装信号处理函数。signal(SIGSEGV, terminate);:为SIGSEGV信号安装信号处理函数。signal(SIGSYS, terminate);:为SIGSYS信号安装信号处理函数。signal(SIGTERM, terminate);:为SIGTERM信号安装信号处理函数。signal(SIGTRAP, terminate);:为SIGTRAP信号安装信号处理函数。signal(SIGUSR1, terminate);:为SIGUSR1信号安装信号处理函数。signal(SIGUSR2, terminate);:为SIGUSR2信号安装信号处理函数。
这段代码的功能是安装信号处理函数,用于捕获和处理不同类型的信号。当程序接收到指定的信号时,会调用terminate函数进行处理。
具体而言,terminate函数会打印接收到的信号编号,并释放视频流捕获对象cap,然后调用exit(1)退出程序。
install_sig_handler函数用于为多个信号注册同一个信号处理函数terminate,使得当这些信号触发时,都会执行相同的处理逻辑。
主循环
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
const int frame_width = 480; // 视频帧宽度
const int frame_height = 480; // 视频帧高度
const int frame_rate = 30; // 视频帧率
char* nbg = "/usr/lib/model/mobilenet_v2_ssd.nb"; // 模型文件路径
install_sig_handler(); // 安装信号处理程序
framebuffer_info fb_info = get_framebuffer_info("/dev/fb0"); // 获取帧缓冲区信息
cap.open(0); // 打开视频设备
if (!cap.isOpened()) {
std::cerr << "Could not open video device." << std::endl; // 如果打开视频设备失败,则输出错误信息并返回
return 1;
}
std::cout << "Successfully opened video device." << std::endl; // 成功打开视频设备,输出成功信息
cap.set(cv::CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, frame_width); // 设置视频帧宽度
cap.set(cv::CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, frame_height); // 设置视频帧高度
cap.set(cv::CAP_PROP_FPS, frame_rate); // 设置视频帧率
std::ofstream ofs("/dev/fb0"); // 打开帧缓冲区文件
cv::Mat frame; // 创建用于存储视频帧的 Mat 对象
awnn_init(7 * 1024 * 1024); // 初始化 AWNN 库
Awnn_Context_t *context = awnn_create(nbg); // 创建 AWNN 上下文
if (NULL == context){
std::cerr << "fatal error, awnn_create failed." << std::endl; // 如果创建 AWNN 上下文失败,则输出致命错误信息并返回
return -1;
}
/* copy input */
uint32_t input_width = 300; // 输入图像宽度
uint32_t input_height = 300; // 输入图像高度
uint32_t input_depth = 3; // 输入图像通道数
uint32_t sz = input_width * input_height * input_depth; // 输入图像数据总大小
uint8_t* plant_data = NULL; // 定义输入图像数据指针,初始化为 NULL
while (true) {
// 从视频设备中读取一帧图像
cap >> frame;
// 检查图像的位深度是否为8位和通道数是否为3
if (frame.depth() != CV_8U) {
std::cerr << "不是8位每像素和通道。" << std::endl;
} else if (frame.channels() != 3) {
std::cerr << "不是3个通道。" << std::endl;
} else {
// 转置和翻转图像以调整其方向
cv::transpose(frame, frame);
cv::flip(frame, frame, 0);
// 将图像大小调整为所需的输入宽度和高度
cv::resize(frame, frame, cv::Size(input_width, input_height));
// 对MobileNetV2 SSD模型进行预处理
plant_data = mbv2_ssd_preprocess(frame, input_width, input_depth);
// 设置AWNN上下文的输入缓冲区
uint8_t *input_buffers[1] = {plant_data};
awnn_set_input_buffers(context, input_buffers);
// 运行AWNN上下文进行模型推理
awnn_run(context);
// 从AWNN上下文中获取输出缓冲区
float **results = awnn_get_output_buffers(context);
// 使用SSD模型进行目标检测并更新图像
frame = detect_ssd(frame, results);
// 将图像大小调整为显示尺寸
cv::resize(frame, frame, cv::Size(DISPLAY_X, DISPLAY_Y));
// 获取帧缓冲区的宽度和位深度
int framebuffer_width = fb_info.xres_virtual;
int framebuffer_depth = fb_info.bits_per_pixel;
// 根据帧缓冲区的位深度将图像转换为兼容格式
cv::Size2f frame_size = frame.size();
cv::Mat framebuffer_compat;
switch (framebuffer_depth) {
case 16:
// 将BGR转换为BGR565格式以适用于16位帧缓冲区
cv::cvtColor(frame, framebuffer_compat, cv::COLOR_BGR2BGR565);
// 将转换后的图像写入帧缓冲区文件
for (int y = 0; y < frame_size.height; y++) {
ofs.seekp(y * framebuffer_width * 2);
ofs.write(reinterpret_cast<char*>(framebuffer_compat.ptr(y)), frame_size.width * 2);
}
break;
case 32:
// 将图像分解为BGR通道并添加一个alpha通道以适用于32位帧缓冲区
std::vector<cv::Mat> split_bgr;
cv::split(frame, split_bgr);
split_bgr.push_back(cv::Mat(frame_size, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(255)));
cv::merge(split_bgr, framebuffer_compat);
// 将转换后的图像写入帧缓冲区文件
for (int y = 0; y < frame_size.height; y++) {
ofs.seekp(y * framebuffer_width * 4);
ofs.write(reinterpret_cast<char*>(framebuffer_compat.ptr(y)), frame_size.width * 4);
}
break;
default:
std::cerr << "不支持的帧缓冲区位深度。" << std::endl;
}
// 释放为plant_data分配的内存空间
free(plant_data);
}
}
这段代码主要实现了以下功能:
-
定义了视频帧的宽度、高度和帧率。
-
指定了模型文件的路径。
-
安装信号处理程序。
-
获取帧缓冲区的信息。
-
打开视频设备,并设置视频帧的宽度、高度和帧率。
-
打开帧缓冲区文件,用于后续操作。
-
初始化 AWNN 库,并分配一定大小的内存。
-
创建 AWNN 上下文。
-
定义输入图像的宽度、高度和通道数,并计算输入图像数据的总大小。
-
声明一个输入图像数据指针。
-
主循环函数,用于不断从视频设备中获取视频帧并进行处理和展示。
具体的步骤如下:
- 使用
cap对象从视频设备中获取一帧图像,并将其存储在frame中。 - 检查图像的位深度是否为8位(CV_8U),如果不是,则输出错误信息。
- 检查图像的通道数是否为3,如果不是,则输出错误信息。
- 对图像进行转置和翻转操作,以调整图像的方向。
- 将图像的大小调整为设定的输入宽度和高度。
- 调用
mbv2_ssd_preprocess函数对图像进行预处理,并将结果存储在plant_data中。 - 将
plant_data设置为AWNN上下文的输入缓冲区。 - 运行AWNN上下文,执行模型推理。
- 使用
detect_ssd函数对图像进行目标检测,得到检测结果的可视化图像。 - 将图像的大小调整为设定的显示宽度和高度。
- 根据帧缓冲区的位深度,将图像转换为与帧缓冲区兼容的格式,并写入帧缓冲区文件。
- 释放
plant_data的内存空间。 - 循环回到第1步,继续获取和处理下一帧图像。
这段代码主要完成了从视频设备获取图像、预处理图像、执行模型推理、目标检测和将结果写入帧缓冲区文件等一系列操作,以实现实时目标检测并在显示设备上展示检测结果。
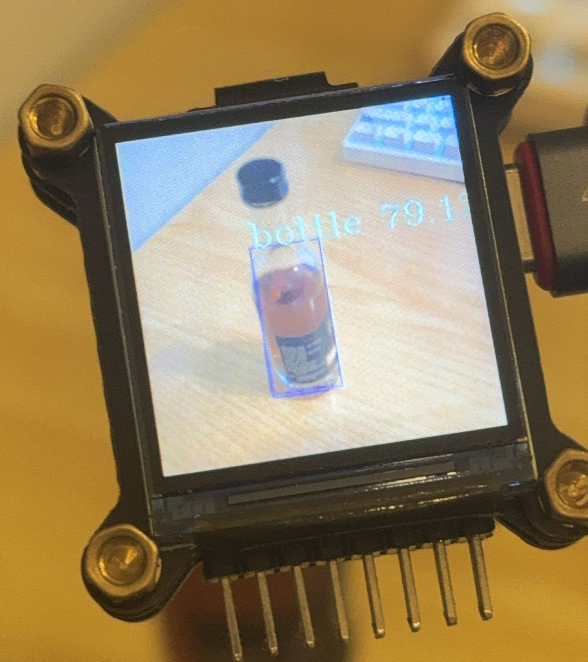
效果展示