T113x系列异构简介
T113s4芯片包含四个CPU。两个主核心Arm A7 CPU,运行Tina Linux(全志自研Linux)系统,为芯片主系统;
一个是RISC-V C906辅助CPU,运行RTOS(全志自研RTOS)系统,主要功能是提供通用算力补充、实现实时控制、辅助 Linux 实现快起和低功耗管理等功能。
还有一个是 DSP HIFI4 核心,主要是用来处理音频算法部分,因为这部分编译器需要企业单独申请,所以无法进行开发使用。
T113家族
如下内容摘自 T113x_Datasheet_V1.3.pdf 版本

T113芯片框图

简单描述

异构子系统框架
参阅 T113x_User_Manual_V1.2.pdf


相关内存分布

MSGBOX 与AMP RPMSG
在 Tina Linux 中,提供 AMP 与 RPMsg 对接 C906
- Linux remoteproc 管理控制 C907
- RPMsg 与 C907 通讯
T113 的异构系统通讯在硬件上使用的是 MSGBOX,在软件层面上使用的是 AMP 与 RPMsg 通讯协议。其中 A7 上基于 Linux 标准的 RPMsg 驱动框架,C906基于 OpenAMP 异构通信框架。
T113 所带有的 A7 主核心与 C906 辅助核心是完全不同的两个核心,为了最大限度的发挥他们的性能,协同完成某一任务,所以在不同的核心上面运行的系统也各不相同。这些不同架构的核心以及他们上面所运行的软件组合在一起,就成了 AMP 系统 (Asymmetric Multiprocessing System, 异构多处理系统)。
由于两个核心存在的目的是协同的处理,因此在异构多处理系统中往往会形成 Master - Remote 结构。主核心启动后启动从核心。当两个核心上的系统都启动完成后,他们之间就通过 IPC(Inter Processor Communication)方式进行通信,而 RPMsg 就是 IPC 中的一种。
在AMP系统中,两个核心通过共享内存的方式进行通信。两个核心通过 AMP 中断来传递讯息。内存的管理由主核负责。

AMP 系统在每个通信方向上都有两个缓冲区,分别是 USED 和 AVAIL,这个缓冲区可以按照 RPMsg 中消息的格式分成一块一块链接形成一个环。

当主核需要和从核进行通信的时候可以分为四步:
(1)主核先从USED中取得一块内存(Allocate)
(2)将消息按照消息协议填充
(3)将该内存链接到 AVAIL 缓冲区中(Send)
(4)触发中断,通知辅助核有消息处理

反之,从核需要和主核通信的时候也类似:
(1)从核先从AVAIL中取得一块内存(Allocate)
(2)将消息按照消息协议填充
(3)将该内存链接到 USED 缓冲区中(Send)
(4)触发中断,通知主核有消息处理。

RPMSG 协议
既然 RPMsg 是一种信息交换的协议,与TCP/IP类似,RPMsg 协议也有分层,主要分为三层,分别是传输层、MAC层和物理层。

其中 MAC层 的 VirtIO 是一种I/O 半虚拟化解决方案,是一套通用 I/O 设备虚拟化的程序,是对半虚拟化 Hypervisor 中的一组通用 I/O 设备的抽象。 提供了一套上层应用与各 Hypervisor 虚拟化设备之间的通信框架和编程接口,减少跨平台所带来的兼容性问题,大大提高驱动程序开发效率。
RPMsg 总线上的消息都具有以下结构,包含消息头和数据两个固定的部分,该消息格式的定义位于drivers/rpmsg/virtio_rpmsg_bus.c中,具体定义如下:
struct rpmsg_hdr {
u32 src;
u32 dst;
u32 reserved;
u16 len;
u16 flags;
u8 data[];
} __packed;
异构系统控制
在异构系统中,不止需要消息的传输,还需要相关控制。例如主核对辅助核心的开启,加载固件,关闭等等。这就需要用到 remoteproc 框架。
remoteproc 框架支持对不同平台,不同架构的处理器进行控制,可以监控辅助核心的运行情况。
对于 T113 来说,remoteproc 用于对 C906 进行生命周期管理,一般来说包含有加载固件、 检测远端处理器是否崩溃等功能。它在加载远端处理器的固件时,会根据固件中定义的 resource table 来申请资源,并创建 VirtIO 设备。
remoteproc 框架抽象出硬件差异,允许不同的平台/架构来控制(开机、加载固件、关机)这些远程处理器,此外,还为支持这种通信的远程处理器添加了 rpmsg virtio 设备。这样,特定平台的 remoteproc 驱动程序只需要提供一些低级处理程序,然后所有 rpmsg 驱动程序就可以正常工作。
作用:
- 从文件系统加载固件
- 准备远程处理器所需资源
- 注册一个
rpmsg virtio设备 - 提供对要提供对远程处理器的生命周期进行管理
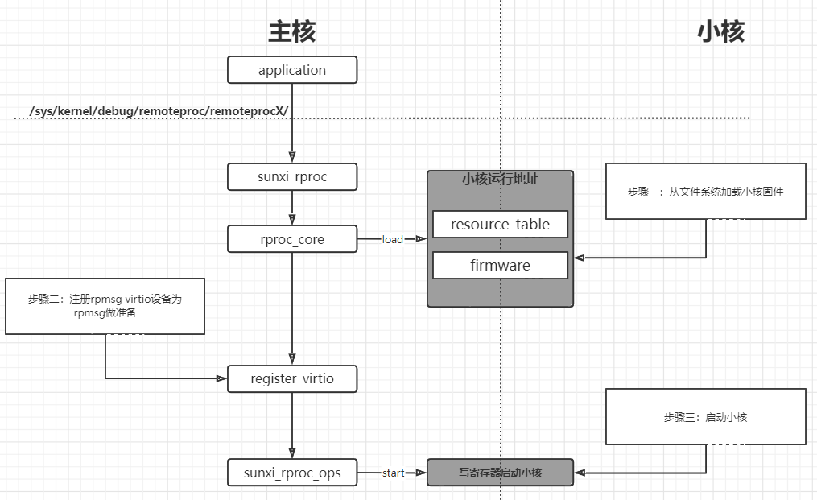
所以固件的加载流程大致如下:
1. 加载固件
1. 调用 firmware 接口获取文件系统中的固件
2. 解析固件的 resource_table 段,该段有如下内容
1. 声明需要的内存(Linux 为其分配)
2. 声明使用的 vdev(固定为一个)
3. 声明使用的 vring(固定为两个)
3. 将固件加载到指定地址
2. 注册 rpmsg virtio 设备
1. 提供 vdev->ops(基于 virtio 接口实现的)
2. 与 rpmsg_bus 驱动匹配,完成 rpmsg 初始化
3. 启动小核
1. 调用 rproc->ops->start
Linux内核配置
首先需要配置设备树,预留 C906 核心内存,buffer 内存,vring 内存等。并正确配置 rproc 与 rpbuf,也不要忘记配置 firmware-name,下面的配置是T113默认提供的示例 为测试固件所使用的地址。不同的固件地址可能不同。
reserved-memory {
#address-cells = <2>;
#size-cells = <2>;
ranges;
/* c906 */
c906_ddr: c906_ddr@42300000 {
reg = <0x0 0x42300000 0x0 0x00600000>;
no-map;
};
/*
* The name should be "vdev%dbuffer".
* Its size should be not less than
* RPMSG_BUF_SIZE * (num of buffers in a vring) * 2
* = 512 * (num of buffers in a vring) * 2
*/
rv_vdev0buffer: vdev0buffer@42900000 {
compatible = "shared-dma-pool";
reg = <0x0 0x42900000 0x0 0x40000>;
no-map;
};
/*
* The name should be "vdev%dvring%d".
* The size of each should be not less than
* PAGE_ALIGN(vring_size(num, align))
* = PAGE_ALIGN(16 * num + 6 + 2 * num + (pads for align) + 6 + 8 * num)
*
* (Please refer to the vring layout in include/uapi/linux/virtio_ring.h)
*/
rv_vdev0vring0: vdev0vring0@42940000 {
reg = <0x0 0x42940000 0x0 0x2000>;
no-map;
};
rv_vdev0vring1: vdev0vring1@42942000 {
reg = <0x0 0x42942000 0x0 0x2000>;
no-map;
};
/* dsp0 */
dsp0ddr: dsp0ddr@42000000 {
reg = <0x0 0x42000000 0x0 0x00100000>;
no-map;
};
dsp0_rpbuf_reserved: dsp0_rpbuf@42244000 {
compatible = "shared-dma-pool";
no-map;
reg = <0x0 0x42244000 0x0 0x8000>;
};
/*
* The name should be "vdev%dbuffer".
* Its size should be not less than
* RPMSG_BUF_SIZE * (num of buffers in a vring) * 2
* = 512 * (num of buffers in a vring) * 2
*/
vdev0buffer: vdev0buffer@42200000 {
compatible = "shared-dma-pool";
reg = <0x0 0x42200000 0x0 0x40000>;
no-map;
};
/*
* The name should be "vdev%dvring%d".
* The size of each should be not less than
* PAGE_ALIGN(vring_size(num, align))
* = PAGE_ALIGN(16 * num + 6 + 2 * num + (pads for align) + 6 + 8 * num)
*
* (Please refer to the vring layout in include/uapi/linux/virtio_ring.h)
*/
vdev0vring0: vdev0vring0@42240000 {
reg = <0x0 0x42240000 0x0 0x2000>;
no-map;
};
vdev0vring1: vdev0vring1@42242000 {
reg = <0x0 0x42242000 0x0 0x2000>;
no-map;
};
/*
* dsp ram addr
*/
dsp0dram: dsp0dram@400000 {
reg = <0x0 0x400000 0x0 0x10000>;
no-map;
};
dsp0iram0: dsp0iram0@420000 {
reg = <0x0 0x420000 0x0 0x8000>;
no-map;
};
dsp0iram1: dsp0iram1@440000 {
reg = <0x0 0x440000 0x0 0x8000>;
no-map;
};
};
mailbox_heartbeat: mailbox_heartbeat@0 {
compatible = "mailbox-heartbeat";
rproc-np = <&c906_rproc>;
mboxes = <&msgbox 6>, <&msgbox 7>;
mbox-names = "tx", "rx";
status = "okay";
};
dsp0_rproc: dsp_rproc@0 {
compatible = "allwinner,hifi4-rproc", "simple-bus";
clock-frequency = <600000000>;
clocks = <&ccu CLK_PLL_PERIPH0_2X>, <&ccu CLK_DSP>, <&ccu CLK_BUS_DSP_CFG>, <&r_ccu CLK_R_AHB>;
clock-names = "pll", "mod", "cfg", "ahbs";
resets = <&ccu RST_BUS_DSP>, <&ccu RST_BUS_DSP_CFG>, <&ccu RST_BUS_DSP_DBG>, <&ccu RST_BUS_MSGBOX1>;
reset-names = "mod-rst", "cfg-rst", "dbg-rst", "msg-rst";
reg = <0x0 0x03000008 0x0 0x04>,
<0x0 0x01700000 0x0 0x40>;
reg-names = "sram-for-cpux", "hifi4-cfg";
mboxes = <&msgbox 0>;
mbox-names = "arm-kick";
memory-region = <&dsp0ddr>, <&vdev0buffer>, <&vdev0vring0>, <&vdev0vring1>,
<&dsp0dram>, <&dsp0iram0>, <&dsp0iram1>;
memory-mappings =
/* < DA len PA > */
/* local SRAM via external bus */
< 0x28000 0x20000 0x28000 >,
/* local SRAM via internal bus */
< 0x400000 0x10000 0x400000 >,
< 0x420000 0x8000 0x420000 >,
< 0x440000 0x8000 0x440000 >,
/* DDR front 256MB */
< 0x10000000 0x10000000 0x40000000 >,
/* local SRAM via internal bus */
< 0x20028000 0x10000 0x400000 >,
< 0x20038000 0x8000 0x420000 >,
< 0x20040000 0x8000 0x440000 >,
/* DDR front 256MB */
< 0x30000000 0x10000000 0x40000000 >,
/* DDR front 1GB */
< 0x40000000 0x40000000 0x40000000 >,
/* DDR front 1GB */
< 0x80000000 0x40000000 0x40000000 >,
/* DDR front 1GB */
< 0xC0000000 0x40000000 0x40000000 >;
id = <0>;
status = "okay";
};
rpbuf_controller0: rpbuf_controller@0 {
compatible = "allwinner,rpbuf-controller";
remoteproc = <&dsp0_rproc>;
ctrl_id = <0>; /* index of /dev/rpbuf_ctrl */
//iommus = <&mmu_aw 5 1>;
memory-region = <&dsp0_rpbuf_reserved>;
status = "okay";
};
rpbuf_sample: rpbuf_sample@0 {
compatible = "allwinner,rpbuf-sample";
rpbuf = <&rpbuf_controller0>;
status = "okay";
};
c906_rproc: c906_rproc@0 {
compatible = "allwinner,c906-rproc";
clock-frequency = <800000000>;
clocks = <&ccu CLK_PLL_PERIPH0_800M>, <&ccu CLK_RISCV>, <&ccu CLK_BUS_RISCV_CFG>, <&ccu CLK_RISCV_RST>, <&ccu CLK_BUS_RISCV>;
clock-names = "pll", "mod", "cfg", "riscv-rst", "riscv-gate";
resets = <&ccu RST_BUS_RISCV_CFG>, <&ccu RST_BUS_MSGBOX2>;
reset-names = "cfg-rst", "msg-rst";
memory-region = <&c906_ddr>, <&rv_vdev0buffer>, <&rv_vdev0vring0>, <&rv_vdev0vring1>;
reg = <0x0 0x06010000 0x0 0x1000>;
reg-names = "c906-cfg";
mboxes = <&msgbox 4>;
mbox-names = "arm-kick";
memory-mappings =
/* DA len PA */
/* DDR for c906 */
< 0x40000000 0x10000000 0x40000000 >;
firmware-name = "amp_rv0.bin";
status = "okay";
};
配置内核驱动
接下来需要配置 kernel 选项,配置驱动。
./build.sh menuconfig
并勾选以下驱动:
> Device Drivers > Mailbox Hardware Support
--- Mailbox Hardware Support
< > Platform MHU Mailbox
< > Altera Mailbox
< > Mailbox Test Client
< > Mailbox Heartbeat driver
<*> Allwinner mailbox support
[ ] Allwinner mailbox support txdone irq
> Device Drivers > Remoteproc drivers
[*] Support for Remote Processor subsystem
<*> Allwinner remoteproc support
<*> Allwinner remoteproc hifi4 boot
<*> Allwinner remoteproc c906 boot
> Device Drivers > Rpmsg drivers
< > RPMSG device interface
< > Qualcomm RPM Glink driver
-*- sunxi amp msgbox driver
< > support send dsp standby msg when suspend.
<*> Virtio RPMSG bus driver
< > Allwinner rpmsg notify driver
<*> Allwinnertech RPMSG hearbeat driver
<*> Allwinner RPMsg tty driver
< > Allwinner RPMsg client sample
<*> sunxi rpmsg ctrl driver
< > Allwinner rpmsg openamp test driver
加载小核固件
测试固件下载地址: https://github.com/DongshanPI/T113M4-DevKit_TinaSDK5
烧录启动系统后,可以在 /sys/kernel/debug/remoteproc/ 节点找到 remoteproc1

我们可以使用 cat 命令检查小核目前的状况
cat /sys/kernel/debug/remoteproc/remoteproc1/state

可以看到提示没有 state 这个节点信息,那么应该是没有默认加载 c906 小核固件。此时我们需要把准备好的固件放置到开发板的 lib/firmware 文件夹内。这里我们使用 adb 上传小核固件。
然后我们将 c906 固件置于 firmware 节点内,并启动固件。
echo amp_rv0.bin > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc1/firmware
echo start > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc1/state
此时可以看到 remoteproc remoteproc1: remote processor c906_rproc is now up,同时查看状态也显示了 running

此时也可以用 stop 命令停止小核运行
echo stop > /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc1/state

AMP SHELL测试小核
Linux端提供了进入从核控制台的功能也就是AMP SHELL,可以直接在Linux终端中,通过 amp_shell 命令进入 C906 异构核心。
首先确保C906 小核已经正常启动,之后使用如下命令进入小核 shell 终端。
root@TinaLinux:~# amp_shell -d /dev/rpmsg_ctrl-c906_rproc@0
便可以启动小核的固件

RTOS系统介绍
系统架构
RTOS 系统是基于FreeRTOS 内核的软件开发包,包含了系统开发用到的内核源码、驱动、工具、组件与应用程序包。通过Makefile 脚本和Kconfig 配置文件,使得用户可以通过menuconfig 进行个性化裁减,编译出一个可以直接烧写到机器上运行的RTOS 系统软件。

RTOS 系统框图如上图,仅从软件的角度来看,从下至上分为内核层、组件层、应用层三个层次。各层次主要内容如下:
- Kernel:内核层包括FreeRTOS 核心系统、文件系统、网络系统、BSP 驱动等。
- Component:组件层包括控制台、多媒体、功耗管理、OTA、音频系统、显示系统、图像采集等。
- APP:应用层包括各种应用demo。
目录结构
rtos
├── board # 包含各SoC板级配置目录
│ └── t113_s3p_c906 # t113_s3p_c906板级配置目录
│ └── t113_s4_c906 # t113_s4_c906板级配置目录
│ └── t113_s4p_c906 # t113_s4p_c906板级配置目录
│ └── XXX # XXX平台板级配置目录
├── envsetup.sh # SDK环境初始化脚本
├── lichee
│ ├── dsp # DSP FreeRTOS系统
│ ├── rtos # ARM/RISC‑V架构的FreeRTOS系统
│ ├── rtos‑components # FreeRTOS公共组件
│ └── rtos‑hal # BSP驱动
└── tools # 打包相关工具脚本目录
所使用RTOS SDK 目录结构如上所示,主要包括如下几个关键目录:
- board:板级配置目录,用于存放芯片方案的配置文件,主要包括系统配置文件sys_config.fex等。
- lichee/dsp:存 放DSP FreeRTOS 系统、组件、应用。
- lichee/rtos:存放ARM/RISC‑V 架构FreeRTOS 系统、组件、应用。
- lichee/rtos‑components:公共组件目录,lichee/dsp 与lichee/rtos 都可以使用该组件。
- lichee/rtos‑hal:BSP 驱动目录,用于存放各种驱动代码。对lichee/dsp 与lichee/rtos 通用。
- tools:工具目录,用于存放编译打包相关的脚本、工具等。
- 下面对lichee/rtos、lichee/rtos‑hal 目录进行详细说明。lichee/dsp 目录与lichee/rtos 目录类似,此处不做介绍。
lichee/rtos 目录
lichee/rtos
├── arch # 处理器架构相关
├── build # 编译临时文件输出目录
├── components # 组件
├── drivers # 驱动
├── include # 头文件
├── kernel # FreeRTOS 内核
├── projects # 方案工程
├── scripts
└── tools # 工具链
lichee/rtos 目录主要包括arch(架构相关)、components(组件)、drivers(驱动)、include (头文件)、kernel(内核)、projects(工程)、toos(工具链) 等目录,下面对常用重要目录分别进行介绍。
- arch 目录 arch 目录主要放置跟SoC 架构相关的内容,每个SoC 单独目录管理,主要包括跟risc‑v 架构相关的ARCH 初始化、中断处理、异常处理、内存映射相关功能的实现。
lichee/rtos/arch/
├── common
└── risc‑v
├── arch.mk
├── c906
├── common
├── e906
├── includes
├── Kconfig
├── Makefile
├── sun55iw3p1
└── sun8iw20p1
- components 目录 components 目录包含allwinner 和第三方的组件。
lichee/rtos/components/
├── aw
│ ├── blkpart
│ ├── bluetooth
│ ├── csi
│ ├── devfs
│ ├── healthd
│ ├── ......
│ ├── watchpoint
│ └── wireless_video
├── common ‑> ../../rtos‑components
└── thirdparty
├── common
├── console
├── cplusplus
├── elmfat
├── finsh_cli
├── ......
└── vfs
- drivers 目录 drivers 目录包含所需的外设驱动,主要包括各外设控制器驱动的具体实现(hal 软连接)以及OSAL 层接口(osal)。
lichee/rtos/drivers/
├── drv
│ ├── cpufreq
│ ├── leds
│ ├── uart
│ ├── ......
│ └── wireless
├── hal ‑> ../../rtos‑hal/
└── osal
- include 目录 include 目录统一管理各模块提供的数据结构定义及函数声明
lichee/rtos/include/
├── arch # 架构相关头文件
├── FreeRTOS_POSIX # POSIX头文件
├── ......
└── vsprintf.h
- kernel 目录 kernel 目录主要包含FreeRTOS 的kernel 源码,全志实现的系统功能相关代码。
lichee/rtos/kernel/
├── FreeRTOS‑orig
│ └── Source
└── Posix
- projects 目录 projects 目录下的每一个子目录代表一个project,实现main 入口,选择不同的project 编译出 来的bin 具有不同功能,每个project 有独立的FreeRTOSConfig 配置。例如T113,其对应于 t113_c906 子目录。
lichee/rtos/projects/
├── Kconfig
├── Makefile
└── t113_c906
├── evb
│ ├── freertos.lds.S
│ ├── ......
│ └── src
│ ├── main.c
│ ├── ......
│ └── FreeRTOSConfig.h
└── Makefile
- tools 目录
- risc‑v 架构这个目录主要包含一些预编译好的交叉编译工具链,目前risc‑v 基于GCC 8.4.0 的交叉编译器。
xxx@xxx:lichee/rtos/tools$ ./riscv64‑elf‑x86_64‑20201104/bin/riscv64‑unknown‑elf‑gcc ‑‑version
riscv64‑unknown‑elf‑gcc (T‑HEAD RISCV Tools V1.10.2 B20201104) 8.4.0
Copyright (C) 2018 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO
warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
lichee/rtos‑hal 目录
lichee/rtos‑hal 目录为BSP 驱动目录,用于存放各种驱动代码。
lichee/rtos/drivers 目录下的rtos‑hal 子目录软链接到该目录,下面对该目录进行介绍。
lichee/rtos‑hal
├── hal # BSP驱动代码
├── include # 驱动相关头文件
└── tools
lichee/rtos‑hal 目录主要包括hal(BSP 驱动代码)、include(驱动相关头文件)等目录,下面分别对其进行介绍。
- hal 目录 hal 目录主要包含各外设驱动代码以及驱动测试代码,source 子目录为驱动代码,test 子目录为驱动测试代码。
lichee/rtos‑hal/hal
├── Makefile
├── source
│ ├── ccmu
│ ├── gpio
│ ├── ......
│ ├── uart
│ └── watchdog
└── test
├── ccmu
├── gpio
├── ......
├── uart
└── watchdog
- include 目录 include 目录主要包含驱动相关头文件以及系统相关接口头文件。
lichee/rtos‑hal/include
├── hal
│ ├── aw‑alsa‑lib
│ ├── aw_common.h
│ ├── ......
│ ├── sunxi_hal_usb.h
│ ├── sunxi_hal_watchdog.h
│ └── video
└── osal
├── hal_atomic.h
├── hal_cache.h
├── ......
├── hal_waitqueue.h
└── hal_workqueue.h
RTOS开发说明
RTOS 环境已集成到Tina Linux 开发环境,通过全志代码服务器对外发布。Tina Linux 开发环境下的rtos 子目录即为RTOS 环境。
Tina 集成了RTOS 的编译、打包功能,而且适用于openwrt、buildroot 等文件系统。这里以T113‑S4 作为例子进行阐述。
关联RTOS方案
在BoardConfig.mk 文件配置RTOS 方案名,关键字段为LICHEE_RTOS_PROJECT_NAME:=xxxxx。目前使用t113_s4_c906_evb1_auto的RTOS 方案。
开发者可以通过修改LICHEE_RTOS_PROJECT_NAME 字段,更改构建RTOS 方案。进入Tina 的rtos 目录(目录结构如下),可以查看到支持RTOS 方案。

├── board
├── envsetup.sh ‑> tools/scripts/source_envsetup.sh
├── lichee
├── out
└── tools
执行以下命令
source envsetup.sh # 配置环境变量
lunch_rtos # 选择编译方案
我们看到可以选择RTOS 方案,即是LICHEE_RTOS_PROJECT_NAME 字段可以配置的RTOS 方案。
1. t113_i_c906_evb1_auto
2. t113_s3p_c906_evb1_auto
3. t113_s3p_c906_evb1_auto_fastboot
4. t113_s3p_c906_evb1_auto_fastboot_video
5. t113_s3p_c906_evb1_auto_non_os
6. t113_s3p_c906_example_demo
7. t113_s4_c906_evb1_auto
8. t113_s4_c906_evb1_auto_fastboot_video
9. t113_s4p_c906_evb1_auto

编译RTOS方案
重新打开一个终端,避免环境变量冲突,在Tina SDK 根目录中,先选择好整体平台方案。
buildroot 方案
1、首先使用如下命令选择整体平台方案
./build.sh config
2、然后RTOS 相关操作命令如下
./build.sh rtos #单独编译RTOS方案
./build.sh rtos menuconfig #修改RTOS配置文件
./build.sh rtos clean #清除RTOS编译中间文件
说明: 执行./build.sh 不会编译RTOS
openwrt 方案
1、首先使用如下命令选择整体平台方案
source build/envsetup.sh #生效环境变量
lunch #选择openwrt方案
2、执行make 会先编译RTOS,再编译Tina
编译快捷命令
在Tina 根目录下,执行了source build/envsetup.sh 后,可以使用RTOS 快捷命令
| 命令 | 命令有效目录 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| mrtos | Tina 环境下任意目录 | 单独编译RTOS 方案 |
| mrtos menuconfig | Tina 环境下任意目录 | 修改RTOS 配置文件 |
| mrtos clean | Tina 环境下任意目录 | 清除RTOS 编译中间文件 |
| crtos | Tina 环境下任意目录 | 进入RTOS 源码目录 |
| crtos‑hal | Tina 环境下任意目录 | 进入RTOS‑HAL 源码目录 |
然后将Tina 环境重新编译和打包,确保RTOS 编译固件amp_rv0.bin 打包到根文件系统中。
说明 buildroot 需要执行./build.sh && ./build.sh pack 命令
说明 openwrt 需要执行make && pack 命令
打包完成后,生产的固件位于tina5.0/out/t113_s4_linux_evb1_auto_uart0.img,可以使用PhoenixSuit 工具烧录到开发板上。
RTOS 固件打包
编译完成后, 生成的镜像文件会自动拷贝到对应平台方案中, 并且rt_system.elf 重名为 amp_rv0.bin 。

